Maintenance and Repair Procedures: Basic Information and Best Practices
Maintenance and repair procedures are critical for businesses and individuals to use their equipment and facilities safely and efficiently. An effective maintenance and repair strategy is essential for preventing breakdowns, reducing costs, and ensuring business continuity. In this article, we will cover the fundamental elements of maintenance and repair procedures and best practices.
What Are Maintenance and Repair?
Maintenance refers to the periodic and planned actions taken to ensure the functionality of equipment and facilities. These actions are generally preventive in nature and aim to prevent failures before they occur.
Repair refers to the actions taken to restore malfunctioning or non-functional equipment and systems to working order. Repair operations typically occur when an issue arises and focus on fixing specific malfunctions.
Importance of Maintenance and Repair Procedures
- Safety: Regular maintenance and quick repairs ensure equipment operates safely, preventing accidents and injuries.
- Efficiency: A good maintenance program ensures equipment runs at maximum efficiency, minimizing production downtime.
- Cost Savings: Preventive maintenance reduces the likelihood of costly repairs and production stoppages caused by unexpected failures.
- Longevity: Extends the lifespan of equipment and facilities, allowing for longer use.
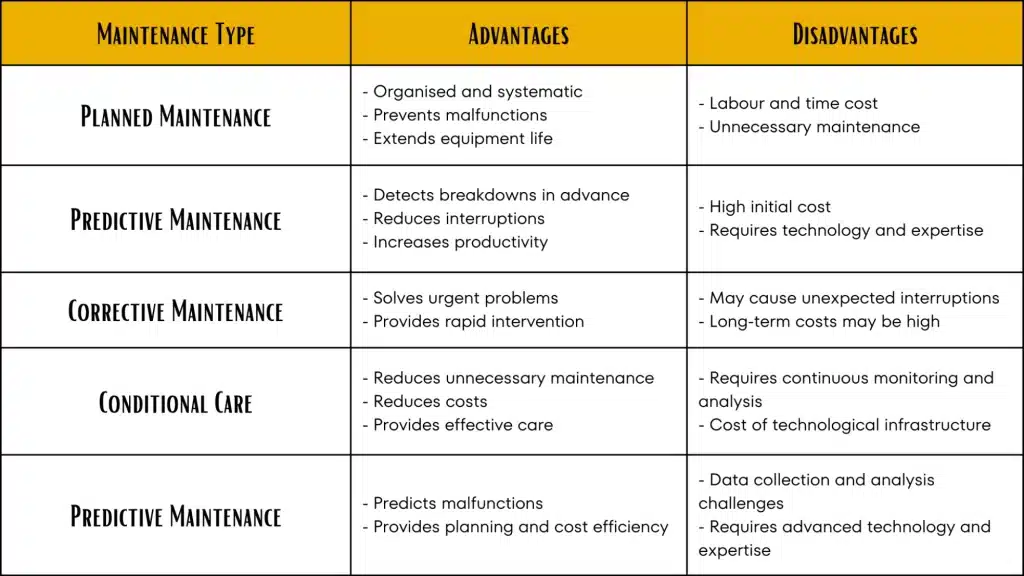
Types of Maintenance
Planned Maintenance (Periodic Maintenance)
Planned maintenance involves regular, systematic maintenance activities performed at specified intervals. This type of maintenance follows the manufacturer’s recommendations and typically adheres to a set schedule. The goal is to extend the equipment’s lifespan and prevent failures. Benefits of planned maintenance include minimal operational disruptions and maintaining optimal equipment performance.
Examples:
- Replacing air conditioning filters every three months
- Lubricating factory machinery monthly
- Annual electrical system inspection
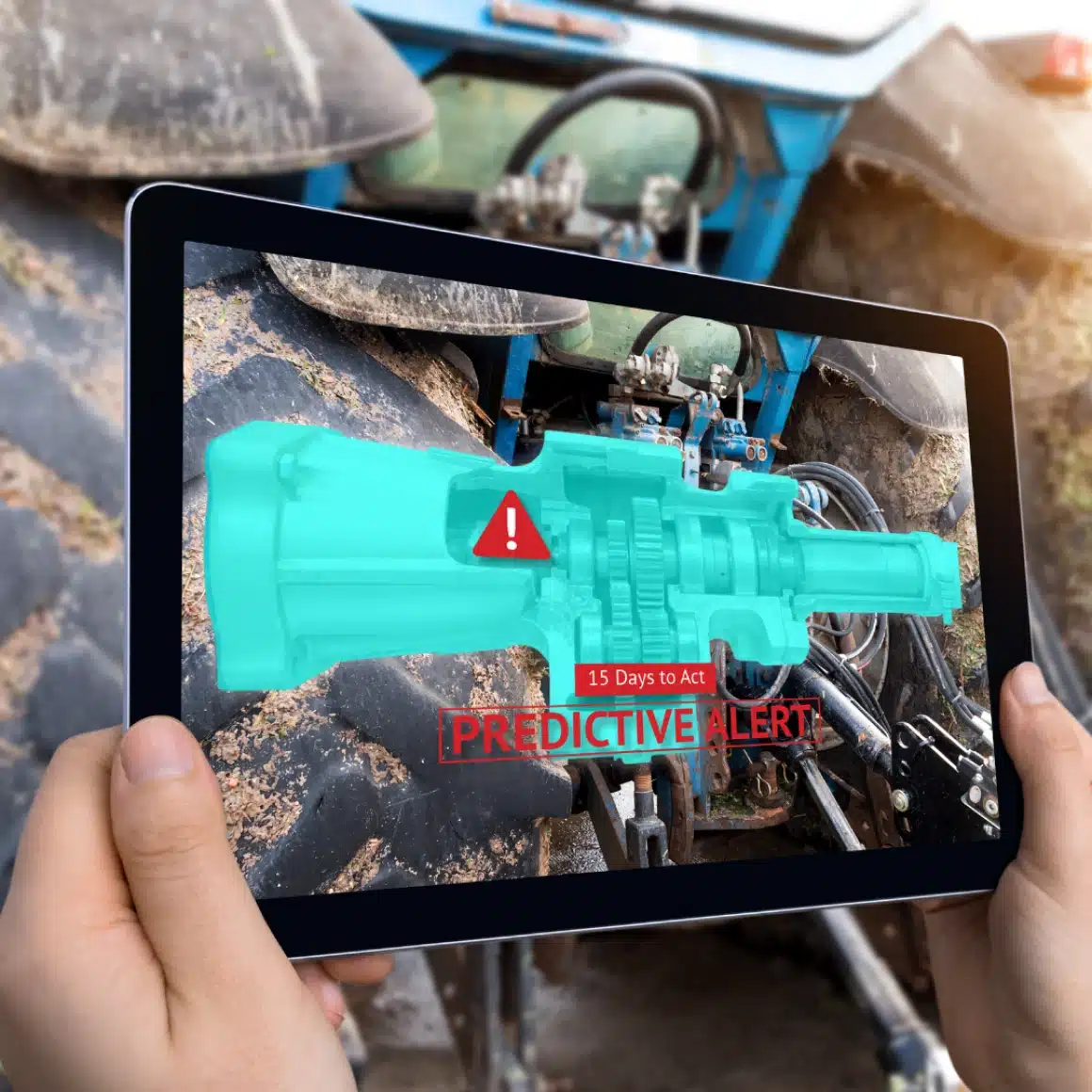
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses various sensors and data analysis software to monitor the condition and performance of equipment. In this type of maintenance, operating conditions and performance data are continuously monitored and analyzed. Maintenance is performed when signs of failure appear, effectively preventing unexpected breakdowns and interruptions.
Examples:
- Detecting wear in machine parts through vibration analysis
- Monitoring excessive heating in electrical panels using thermal cameras
- Identifying wear in engine components through oil analysis
Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance is performed when equipment fails or loses functionality. It typically requires urgent intervention and involves repairing or replacing faulty components. Corrective maintenance ensures rapid problem resolution, minimizing the negative impact of unexpected failures on operations.
Examples:
- Replacing a broken machine part
- Repairing a device that has stopped working due to an electrical fault
- Fixing a leaking pipe
Condition-Based Maintenance
Condition-based maintenance involves evaluating the real-time condition of equipment. Sensors and monitoring systems collect and analyze data. Based on this analysis, the need for maintenance is determined. Condition-based maintenance reduces unnecessary maintenance activities, lowering costs and improving maintenance efficiency.
Examples:
- Performing maintenance when a motor exceeds a certain temperature threshold
- Inspecting machines when vibration levels exceed a specific value
- Maintaining a hydraulic system when the oil level falls below a certain level
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance aims to predict future failures using historical data and statistical analysis. This type of maintenance uses various analytical tools and models to foresee breakdowns and take preventive measures in advance. Predictive maintenance minimizes disruptions and costs caused by failures.
Examples:
- Using machine learning algorithms to predict equipment failures
- Optimizing maintenance schedules by analyzing historical maintenance data
- Identifying potential failure scenarios using Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Steps in Maintenance and Repair Procedures
- Planning: Prepare a detailed plan for maintenance and repair activities. Determine which equipment needs maintenance and when, and ensure necessary materials and personnel are available.
- Monitoring and Inspection: Regularly check and monitor the condition of equipment. Use sensors and data analysis software for predictive maintenance.
- Implementation: Perform planned maintenance and repair activities on time and correctly. Adhere to technical instructions and safety procedures.
- Evaluation: Assess the effectiveness of maintenance and repair activities. Perform post-process performance measurements and plan necessary improvements.
- Documentation: Document all maintenance and repair activities in detail. These records serve as a reference for future maintenance planning.
Best Practices
- Regular Training: Regularly train maintenance and repair personnel to keep them informed of the latest techniques and safety procedures.
- Use of Technology: Optimize maintenance processes by using modern sensors, IoT devices, and data analysis software.
- Spare Parts Management: Keep critical spare parts in stock to enable rapid intervention in case of failure.
- Collaboration: Good collaboration and communication between different departments enhance the efficiency of maintenance and repair processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and improve maintenance and repair processes to make them more efficient.
Have you received sufficient information about “Maintenance and Repair Procedures“?
repairist is here to help you. We answer your questions about the Maintenance Management System and provide information about the main features and benefits of the software. We help you accessthe repairist demo and even get a free trial.
Aybit Technology Inc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Condition-based maintenance monitors the real-time condition and performance of equipment. Data collected through sensors and monitoring systems are analyzed to determine when maintenance is needed. This method reduces unnecessary maintenance activities and lowers costs.
You should choose the most suitable type of maintenance based on your business needs and the operating conditions of your equipment. Planned maintenance provides a regular and systematic approach, while predictive and condition-based maintenance offer more technology-focused and data-driven solutions. Predictive maintenance uses advanced analysis and machine learning to predict failures. The best results come from a suitable combination of these maintenance types.
Maintenance and repair activities should be carried out by trained and experienced technicians or engineers. Regular training and certification programs ensure maintenance personnel are informed about the latest techniques and safety procedures.